Problem 1
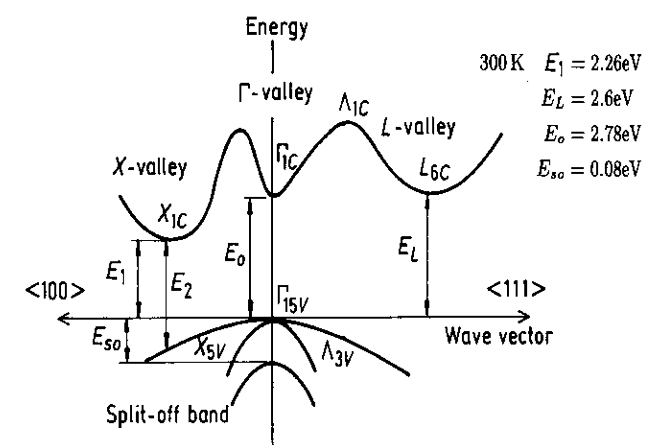
A simplified bandstructure of GaP is shown below.

(a) What is the bandgap of this semiconductor? Is it a direct semiconductor or an indirect semiconductor?
(b) Label the light hole band and the heavy hole band.
(c) Sketch the density of states for this semiconductor. Use the bandstructure to decide if the density of states rises faster in the valence band or in the conduction band. Label the valence band edge, the conduction band edge, and the Fermi energy in your drawing.
(d) A pn-diode is made from GaP where the p-side is heavily doped and the n-side is lightly doped. Draw the band diagram (conduction band, valence band, and Fermi energy) for a reverse bias.
Problem 2
(a) Make a drawing of a light-emitting diode including the metal contacts.
(b) Explain what you have to do to efficiently couple the light out of the diode.
(c) Why do laser diodes have a threshold current while light-emitting diodes do not?
(d) What determines the center wavelength of the light that an LED emits? There is some spread of wavelengths around this center wavelength. What causes this spread?
Problem 3
A drawing of a transistor from Wikipedia is shown below.
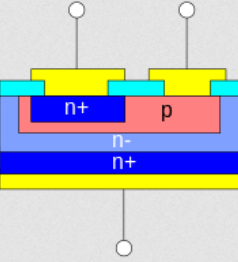
(a) What kind of transistor is this? Label the three contacts.
(b) What is the purpose of the two n+ regions? What is the purpose of the light blue regions? What is the purpose of the yellow regions?
(c) Where do you expect there will be a Schottky contact in this structure?
(d) If you shine light on this transistor and measure the voltage between the two upper contacts, what voltage will you measure? What polarity will this voltage have, positive on the p contact or negative on the p contact? Explain your reasoning.
Solution
Problem 4
(a) Draw an $p$-channel MOSFET showing the source, drain, gate, and body contacts.
(b) The MOSFET is biased in saturation. Draw the depletion region in your drawing from part (a). Put + and - signs in the drawing to show how the charge is distributed.
(c) A voltage is applied between the source and the body. Explain how this shifts the threshold voltage. Which direction is the threshold voltage shifted and how far can it be shifted?
(d) Explain what latch-up is in CMOS circuits.