|
| |
Physical Constants
Quantity |
Symbol |
Value |
Units |
| electron charge |
e |
1.60217733 × 10-19 |
C |
| speed of light |
c |
2.99792458 × 108 |
m/s |
| Planck's constant |
h |
6.6260755 × 10-34 |
J s |
| reduced Planck's constant |
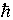
|
1.05457266 × 10-34 |
J s |
| Boltzmann's constant |
kB |
1.380658 × 10-23 |
J/K |
| Gravitational constant |
G |
6.6726 × 10-11 |
N m2/kg2 |
Acceleration of gravity
at earth's surface |
g |
9.807 |
m/s2 |
| electron mass |
me |
9.1093897 × 10-31 |
kg |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant |
σ |
5.67051 × 10-8 |
W m-2 K-4 |
| Bohr radius |
a0 |
0.529177249 × 10-10 |
m |
| proton mass |
mp |
1.6726231 × 10-27 |
kg |
| neutron mass |
mn |
1.6749286 × 10-27 |
kg |
| atomic mass constant |
mu |
1.6605402 × 10-27 |
kg |
| permeability of vacuum |
μ0 |
4π × 10-7 |
N A-2 |
| permittivity of vacuum |
ε0 |
8.854187817 × 10-12 |
F m-1 |
| Coulomb constant |
k |
8.98755 × 109 |
m F-1 |
| Avogado's constant |
NA |
6.0221367 × 1023 |
mol-1 |
π = 3.141592653589793238462643383279502884197
Fundamental Physical Constants (National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA)
SI units
Measurement uncertainty
|