Problem 1
State if the dominant current mechanism is drift, diffusion, thermionic emission, or tunneling in the following cases.
(a) A JFET in the linear regime.
(b) An LED when it is emitting light.
(c) The gate current of a MESFET.
(d) An Ohmic contact between a metal and a p+ semiconductor.
(e) The base-emitter current of a pnp bipolar transistor in forward active mode.
(f) The subthreshold current of a MOSFET.
(g) A Zener diode in forward bias.
Problem 2
Consider a pn diode at zero bias. The n-side is more heavily doped than the p-side.
(a) Plot electron concentration, the hole concentration, and the electric field. Indicate where the edges of the depletion regions are. Use a linear scale (not logarithmic) for the plots.
(b) What are the formulas for drift current density and diffusion current density?
(c) Make four plots above each other of the electron drift current density, the hole drift current density, the electron diffusion current density, and the hole diffusion current density.
Problem 3
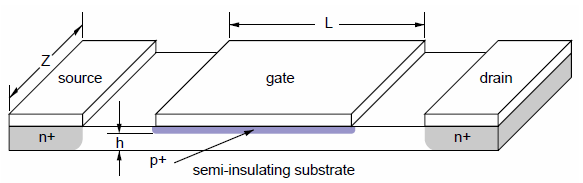
An n-channel JFET is shown below.

(a) How could you experimentally determine the doping of the channel?
(b) If you know the doping of the channel, how could you experimentally determine the distance $h$?
(c) The drain contact should not be to close to the gate contact and not too far. What happens when it is too close and what happens when it is too far?
(d) If the JFET is biased in saturation, where is the highest electric field and which way is the field pointing?
Problem 4
Consider an npn bipolar transistor in forward active mode.
(a) The base width of the transistor should not be too thin or too thick. What happens if it is too thin and and what happens if it is too thick?
(b) The doping of the collector should not be too high or too low. What happens if it is too high and what happens if it is too low?
(c) What limits the maximum operation frequency of a bipolar transistor?
(d) When a bipolar transistor is used as a amplifier, it is better suited to measuring current rather than voltages. Why is this?
Quantity | Symbol | Value | Units | |
| electron charge | e | 1.60217733 × 10-19 | C | |
| speed of light | c | 2.99792458 × 108 | m/s | |
| Planck's constant | h | 6.6260755 × 10-34 | J s | |
| reduced Planck's constant | $\hbar$ | 1.05457266 × 10-34 | J s | |
| Boltzmann's constant | kB | 1.380658 × 10-23 | J/K | |
| electron mass | me | 9.1093897 × 10-31 | kg | |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | σ | 5.67051 × 10-8 | W m-2 K-4 | |
| Bohr radius | a0 | 0.529177249 × 10-10 | m | |
| atomic mass constant | mu | 1.6605402 × 10-27 | kg | |
| permeability of vacuum | μ0 | 4π × 10-7 | N A-2 | |
| permittivity of vacuum | ε0 | 8.854187817 × 10-12 | F m-1 | |
| Avogado's constant | NA | 6.0221367 × 1023 | mol-1 |