Problem 1
Consider a p-i-n (p-doped - intrinsic - n-doped) junction.
(a) Draw the charge density of an unbiased p-i-n junction.
(b) Draw the electric field in an unbiased p-i-n junction.
(c) Draw the band diagram of the p-i-n junction. Keep in mind that the slope of the conduction band and valence band should be proportional to the electric field.
(d) Draw the electron and hole concentrations in the p-i-n junction.
Solution
Problem 2
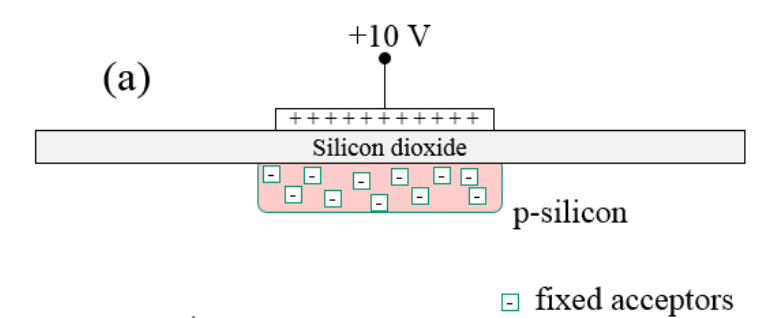
This is a drawing of a pixel of a CCD camera before light strikes it.

(a) What happens when light strikes the pixel?
(b) How does the charge on the metal side of this MOS capacitor change when light strikes the pixel?
(c) How does the camera know the color of the light?
Problem 3
(a) Draw a cross section of a p-channel MOSFET showing the source, drain, gate, and body contacts.
(b) Draw the band diagram for the p-channel MOSFET in weak inversion along a line that goes from the gate metal to the body.
(c) Is the drain-body diode in forward bias or reverse bias when the transistor is in saturation?
(d) How could you experimentally determine the threshold voltage?
Problem 4
Consider an npn bipolar transistor in foward active mode.
(a) Make four plots above each other of the electron drift current, the hole drift current, the electron diffusion current, and the hole diffusion current along a line from the emitter, through the base, to the collector. Indicate where the edges of the depletion regions are.
(b) To calculate the emitter efficiency, three points on these plots are used. Which three points are they?
(c) How would you calculate the base transport factor from these plots?
(d) What limits the maximum allowed collector-emitter voltage? How could you modify the transistor to make the maximum allowed collector-emitter voltage larger?
Quantity | Symbol | Value | Units | |
| electron charge | e | 1.60217733 × 10-19 | C | |
| speed of light | c | 2.99792458 × 108 | m/s | |
| Planck's constant | h | 6.6260755 × 10-34 | J s | |
| reduced Planck's constant | $\hbar$ | 1.05457266 × 10-34 | J s | |
| Boltzmann's constant | kB | 1.380658 × 10-23 | J/K | |
| electron mass | me | 9.1093897 × 10-31 | kg | |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | σ | 5.67051 × 10-8 | W m-2 K-4 | |
| Bohr radius | a0 | 0.529177249 × 10-10 | m | |
| atomic mass constant | mu | 1.6605402 × 10-27 | kg | |
| permeability of vacuum | μ0 | 4π × 10-7 | N A-2 | |
| permittivity of vacuum | ε0 | 8.854187817 × 10-12 | F m-1 | |
| Avogado's constant | NA | 6.0221367 × 1023 | mol-1 |