Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil of wire that is used to generate a magnetic field. In the limit of a long solenoid, the magnetic field inside the solenoid is uniform and is given by the formula,
$\large B= \mu_0 nI$ [T].
Here $n$ is the number of turns per meter along the length of the solenoid, $I$ is the current, and $\mu_0$ is the permeability constant.
On the Wikipedia page for a solenoid, the following image is used to show what the magnetic field pattern looks like at the ends of the solenoid.
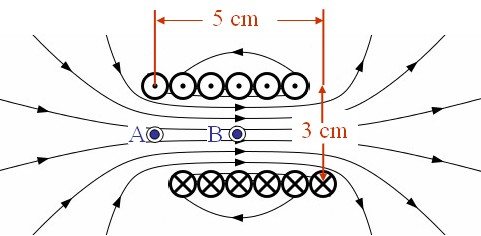
There are 6 turns in 5 cm in this coil, thus $n=120$ turns per meter. If a current of 1 A flows through the coil, the formula for the field in a long solenoid predicts that the field inside the solenoid is,
$\large B= \mu_0 nI= 4\pi \times 10^{-7} \times 120 \times 1 = 4.8 \times 10^{-5}$ [T].
Use the Biot-Savart law app to determine the magnetic field at points A and B.