|
| |
Crystal structure
This page contains a list of definitions and concepts you should know for the exam.
Structural materials are used to build things and their mechanical properties are of primary importance. Examples are concrete, steel, and wood.
Functional materials are used for something other than structural applications. They can be used as sensors, light emitters, solar cells, batteries, or computer components.
An amorphous material is one where the arrangement of the atoms is not periodic. This can happen if a material is melted and them cooled down quickly. An example of an amorphous material is window glass.
In a crystal, atoms are arranged in straight rows in a three-dimensional periodic pattern. Many materials contain crystals if examined on the microscopic scale. The size of the crystals can range from nanometers to meters depending on how the material is prepared. Devices such as solid-state transistors, lasers, solar cells, and light-emitting diodes are often made from single crystals. Many materials, including most metals and ceramics, are polycrystaline. This means there are many little crystals packed together where the orientation between the crystals is random. Even though not all solids are crystals, we will spend most of our time studying crystals since the translational symmetry makes them easier to describe mathematically. Describing the behavior of more complicated materials usually builds on the understanding that has been acquired by studying crystals.
A Bravais lattice is a periodic arrangement of points. In thre dimensions there are 14 Bravais lattices.
A small part of the crystal that can be repeated to form the entire crystal is called a unit cell. A primitive unit cell is the smallest collection of atoms that can be repeated on the Bravais lattice to form a crystal. Sometimes these primitive unit cells have odd shapes and crystallographers define a conventional unit cell that contains more atoms but has a simpler shape. The conventional unit cells are shown in the list of Bravais lattices.
Asymmetric unit
| 
Primitive unit cell
| 
Conventional unit cell
| 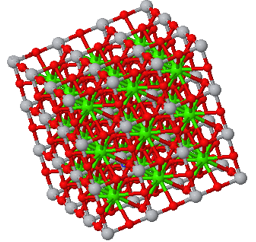
Crystal
|
Some common crystal structures you should know
Suggested Reading
Kittel Chapter 1: Crystal Structure or R. Gross und A. Marx: Kristallstrucktur 1.1 - 1.2
|